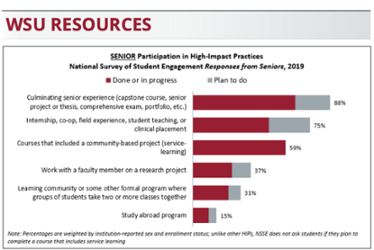
Marian University (Indianapolis, IN) has an institutional effort to increase student participation in internships and field experiences. NSSE results helped the University assess these important career-related HIPs. Participation in these HIPs has grown by 16 percentage points since 2015. In NSSE 2019, 82% of Marian’s seniors reported participating in an internship. This program’s success has largely been driven by Marian’s institutional culture of cross-department support as well as an institutional focus on remaining learning centered. Housed within The Exchange, Marian’s career development office, the program comprises an institutional system for internships that includes partnerships between academic departments and the Office of Institutional Research, which oversees the administration of NSSE and strives to make both quantitative and qualitative data accessible to all stakeholders through presentations across campus and intranet access. Marian is also committed to assessment to ensure equity and quality. For example, they plan to examine which students participate in internships and how their engagement outcomes compare to those of nonparticipants.
California State University San Marcos (San Marcos, CA) places a priority on High-Impact Practices (HIPs) such as the first-year seminar, internships, and undergraduate research. Emblematic of this institutional emphasis, a HIP task force composed of faculty, staff, and administrators with interest or involvement in campus HIPs used NSSE data to disaggregate student participation in HIPs by student major and demographic characteristics. These data helped them identify student groups less likely to participate in HIPs and to direct them to HIP opportunities. CSUSM stakeholders have used NSSE data to measure the overall effect of efforts to improve HIP participation, and the data suggest interventions are working. Encouragingly, results from subsequent NSSE administrations indicated that HIP participation has increased. Also, using common HIP data has facilitated cross-division collaboration at the university, as all entities work from the same data points and share a common framework for conversations to identify needs and plan interventions. Read more about CSUSM in Lessons from the Field, Volume 4.
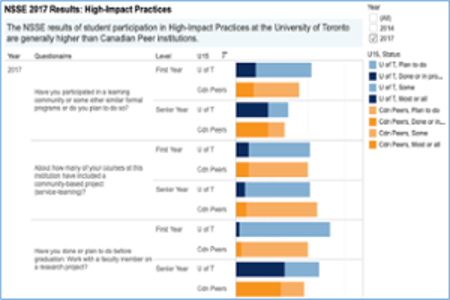
Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis (Indianapolis, IN) stakeholders are interested in increasing participation in and measuring the quality of High-Impact Practices (HIPs). One key campus initiative targeting this goal is the RISE Initiative—Research, International experiences, Service-learning, and Experiential learning—which provides maps for students to enroll in RISE courses and resources for faculty (e.g., taxonomies and funding for course development). To measure the quality of RISE, the Office of Institutional Research and Decision Support uses retention data, follow-up surveys, qualitative interviews, and NSSE data. Triangulated with data from the other sources, NSSE data help illuminate the relationship between HIP participation and desired student outcomes. NSSE results have indicated that, among first-year and senior students, RISE participation is related to increases in engagement behaviors associated with Higher-Order Learning and Discussions with Diverse Others.